Secure Socket Layer (SSL) is a suit of protocol that resides in the transport
layer of the OSI reference model.
SSL is built into all major browsers and installing a digital certificate activates SSL
capabilities. SSL is designed to ensure
the security requirements of PKI, through the use of digital
certificates and public key and private key encryptions.
Note that both symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption are used in
the communication. In fact message
is encrypted and decrypted using symmetric key algorithm because it is much
faster. Asymmetric key algorithm is
predominantly used for the private exchange of the symmetric key.
In a client-server architecture, when a client requests
a secure session from a server, client and server undergo a handshake process
(for the exchange of private key):
- Client
sends a request to the server to establish secure connection
- Server
forwards the client its digital certificate (essentially its public key)
- Client
generates a key called "secret key" (also called "session
key") on the fly (generated by client's computer at that instance)
- Client
encrypts the session key using server's public key and product is digital
envelope (process 4 in the diagram)
- Client
forwards the digital envelope to the server
- Server
decrypts the digital envelope using its private key to retrieve the
session key (process 5 in the diagram)
At this point client and the server have established between themselves a
session key that is going to be used as a symmetric key for encrypting
messages. This is called a session key
because it lasts for communication during a session that could be as long as a
number of hours and as short as a few minutes, depending on how the server is
configured. An inactive session usually
times out after about 20 minutes.
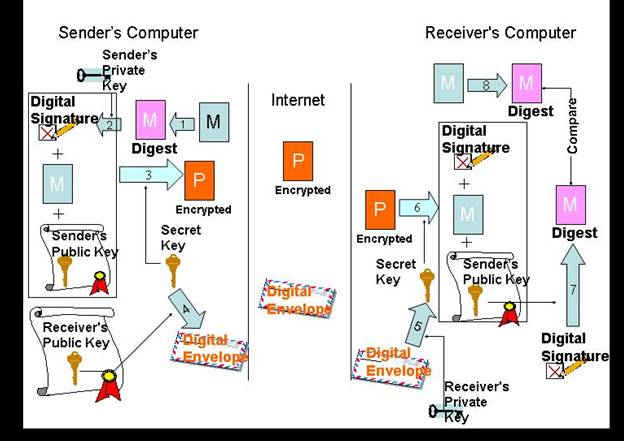
Having established the connection and the session key, exchange of
message follows the following steps:
- One-way
hash function is used by the client to generate message digest
(MD) from the message
- Client
uses its private key to encrypt MD and resulting product is digital signature
- Client
packages the digital signature, the message, and its public key and
encrypts the package using the established session key and forwards the
encrypted package to the server over the Internet
- Server
decrypts the encrypted package using the established session key to
recover the package i.e. the message, digital signature of client, and
client's public key
- Server
recovers MD by decrypting digital signature of client using client's
public key
- Server
also generates MD from the message using the one-way hash function
- Server
compares the two versions of MD
Hence through the use of SSL we have ensured:
- Authentication: MD of
message is recovered by decrypting client's digital signature for the
message. Success and positive
comparison ensures the integrity of MD, which in turn prove that MD must
have been encrypted with Client's private key and hence the client must
have sent the message
- Integrity: Server
ensures the integrity of the message or detects lack of integrity of the
message through comparison of the two versions of MD. If they compare, message has not been
altered in transit
- Privacy: Exchange
of message takes place in a secure environment through encryption using
the session key. The content of the
message is only visible to the client and the server.
- Non-repudiation: MD
of message is recovered by decrypting client's digital signature for the
message. Success and positive
comparison ensures the integrity of MD, which in turn prove that MD must have
been encrypted with Client's private key.
Client can not later repudiate (deny) from having sent the message
because he is the only one holding that private key
Also see the following for more:
http://wp.netscape.com/eng/ssl3/ssl-toc.html
http://wp.netscape.com/eng/ssl3/index.html
http://www2.psy.uq.edu.au/~ftp/Crypto/
http://www.articsoft.com/security%20education.htm
|
How
would you know you are making SSL-secured connection to the server? Indicate
two ways. |
|
|
|
SSL's
symmetric encryption uses DES algorithm and the key could be between 40 and
128 bits (128-bit encryption is now standard). Imagine the strength of a 40-bit
encryption. By what factor is a
128-bit encryption stronger than a 40-bit encryption? |
|
|
|
How
do the client (browser) and the server decide what size of key to use for the
session key? |
|
|
|
For using SSL, does
the client side need to have a digital certificate)? If so, then why can I
access secure Web sites from my computer when seemingly I do not have a
certificate? If it is not needed, then how does the protocol work? |
|
|
|
What
is TLS? |
|
|