LEARNING FOR "MANAGING INFORMATION AND KNOWLEDGE IN AN E-BUSINESS"
In this piece of learning, we'll look at the necessary aspects of information and knowledge management infrastructures required in the development of an e-Business opportunity. We'll do this by:
- Investigating the idea of an information management infrastructure
- Looking at how an information and knowledge management (IKM) infrastructure is developed
- Considering technologies for the creation of interfaces to these infrastructures
- Looking at how interfaces to these infrastructures are created
What is an Information Management Infrastructure?
In his book "Business @ The Speed of Thought", Bill Gates refers to an Information Management Infrastructure as a kind of digital nervous system - it's designed to get the right information to the right part of an organisation at the right time.
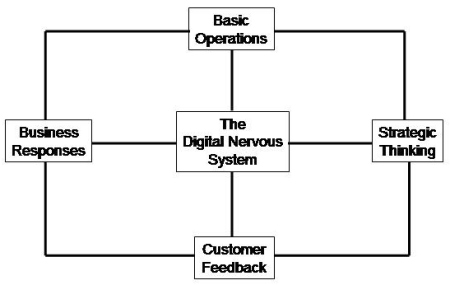
He produced this diagram to demonstrate the point, and to show the relationships between it and important components of the business.
Think back to the Enterprise Solutions Framework we saw a few weeks ago. We can show how an Information Management Infrastructure creates a digital nervous system through the addition of a number of characteristic technologies.
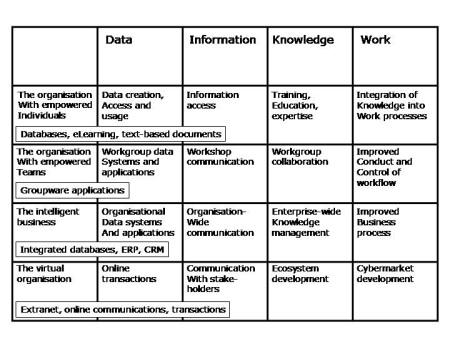
If we integrate the processes with those technologies, the information and knowledge management infrastructure supports the continual process of transforming data and information into organisational knowledge for distribution around the organisation.
How is an Information and Knowledge Management Infrastructure developed?
In order to be able to create an Information and Knowledge Management Infrastructure, the e-Business needs to be able to identify knowledge sources from data sources, be able to capture that knowledge in information systems, and be able to create an enabling mechanism that allows for the retrieval of that knowledge.
In many instances, a database provides the fundamental building block for an IKM infrastructure. There are advantages and disadvantages to their use, and they break down into several kinds:
Older styles of database concepts included the Hierarchical database structure, where the relationship between records is one-to-many - this rigid style of approach doesn't suit today's e-Business needs. Network database structures support many-to-many relationships, but they tend to be inflexible and inefficient in their design. High use is made of the Relational database concept, because this is highly flexible and supports all varieties of relationship.
Two varieties of database concept that are becoming increasingly common include the Object-oriented database, which deals with data property storage and processing method from an object-driven approach - this approach supports integration between radically different systems - and the Hypermedia Database, which use hyperlinks (like in web pages) to relate components. Hypermedia databases are naturally compatible for the Internet and offer an opportunity to neatly integrate with commonly used protocols on the Internet.
- Now do Task 1 from the Tasks Page
As we mentioned, knowledge can be captured in databases, but there are also opportunities to capture "knowledge" in file directory structures, expert systems, case-based reasoning tools and other so-called "intelligent structures". Within the e-Business, these systems are web-enabled, providing powerful interfaces into the knowledge management system and thus creating e-Business applications.
There are a variety of Knowledge Management systems that are commonly used in e-Business ventures, and these include some of the following
An Enterprise Resourcing Planning system (including products from companies such as SAP, SAS and Oracle) re-engineers the flow of data and information around an organisation and provides participants in the venture with access to rich information. A combination of "Directory Services" and Middleware technologies are used to support this kind of system
Directory Services maintain databases on users of the system, what services are available to them, and hardware and software is available on the network. They often provide some kind of search mechanism so that users can find information and services available to them.
In the e-Business, Directory Services might be used to create directories of email addresses, user identities and their associated passwords, security documentation for participants in the knowledge network, and perhaps data resources.
Middleware refers to the applications that integrate back-office systems with front-end desktop and Internet applications. The role of middleware is to provide watertight, reflexive and real-time communication between organisational systems.
- Now do Task 2 from the Tasks Page
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems
From a technical perspective, a CRM system acquires information from all possible sources by registering every customer 'event'. The e-Business will use it to improve customer relationship. A number of tools are used in this system.
A data warehousing tool is used as a store of historical data obtained from all of the organisations systems. A data mining tool allows the analysis of such data through simple "database-style" queries, complex queries, modelling and forecasting. Data mining is often performed by "intelligent" tools, such as intelligent agents or association analysis tools. We'll talk more about the business issue of CRM in the section on CRM.
- Now do Task 3 from the Tasks Page
Intranets for Knowledge Management
An intranet should be designed to allow users to share resources. They usually have an Internet interface (often based around a browser) allowing for easy acquisition of information. Sometimes they are used to share information and communicate with e-Business partners who reside outside the traditional boundary of the organisation.
Intranets should save time and effort in providing service to people within the e-Business and improve customer service. They increase communication and knowledge sharing, assist group-working, and improve the efficiency, and effectiveness of business activities.
Intranets need to be useful and usable, they need to be tough, integrate with other systems, be secure and most of all they must be something that users need.
An Extranet is an intranet which includes e-Business trading and supplying partners as users, and possibly extends its reach outside of the boundary of the organisation.
Groupware for Knowledge Management
Groupware provides resource for a team of workers irrespective of their location. Commonly used applications in e-Business knowledge management include email, collaborative tools, bulletin boards and workflow management tools.
- Now do Task 4 from the Tasks Page
Issues in creating Interfaces to these Infrastructures
When an e-Business looks to create interfaces to these IKM infrastructures, participants need to consider issues of security, technology choice, how systems are integrated, how the systems are developed (and maintained) and managed.
The commonly used technologies use in the development of interfaces to IKM infrastructures include HTML and DHTML, VR languages, XML and XSL, Java technology, scripting languages (such as JavaScript) and approaches such as the Common Gateway Interface (CGI).
An interface with an IKM infrastructure has to be accepted by its users, and this suggests that a participative approach to the design and implementation of the interface should be adopted. Such an interface must be integrated with all applications used by the user, transparent (so that users don't know they're using different systems), customised for each user and totally reliable. Sometimes these interfaces are known as Enterprise Portals.
IKM Infrastructures can fail, if they don't keep up with and match the size of the organisation. They may cause information overload for participants. They can cause organisations to hoard knowledge irrespective of its value or age. And users may not actually know what to do with the resources available to them anyway.
- Now do Task 5 from the Tasks Page