What is SET?
Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) is a suit of protocol that has been
developed and promoted by a consortium of Visa and MasterCard to ensure
security of online financial transactions.
The idea with SET is that a combination of digital certificates is used
to ensure the security requirements of transactions between the consumer,
merchant, financial institutions, and the payment gateways.
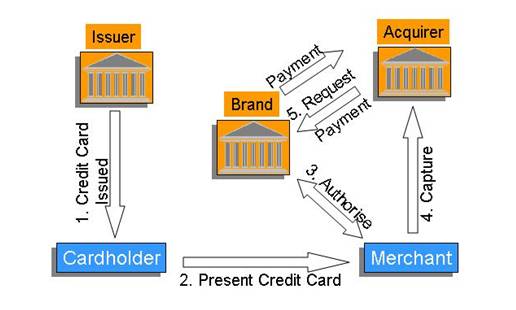
In absence of SET credit card transactions between the consumer,
merchant, and financial institutions take place as indicated in the diagram:
- Issuer
(could be consumer's High street bank) issues consumer with the credit
card
- Cardholder
(consumer) presents the merchant with his credit card for payment along
with the order
- Merchant
requests and receives authorisation of payment from the credit card brand
(could be Visa, MasterCard, American Express, etc) before processing the
order
- Having
received authorisation from the brand, merchant initiates the process of
capture of monitory funds through the acquirer (could be Merchant's High
street bank)
- Acquirer
forwards authorisation details to the brand and requests settlement from
the brand
- Having
received payment from the brand, acquirer credits Merchant's account with
the funds
- Brand
bills the consumer for the funds
The process described above is followed whether or not transaction is
online. One major problem with this
process is that consumer's sensitive information (credit card information) is
divulged to the merchant with potential privacy implications for the consumer. There is also the issue of authentication of
both the consumer (is the consumer the true cardholder) and the merchant (is
the merchant who the consumer believes to be or is the Web front merely a front
to the adversary's website). SET is designed
to overcome these issues through authentication of all bodies with the use of
digital certificates.
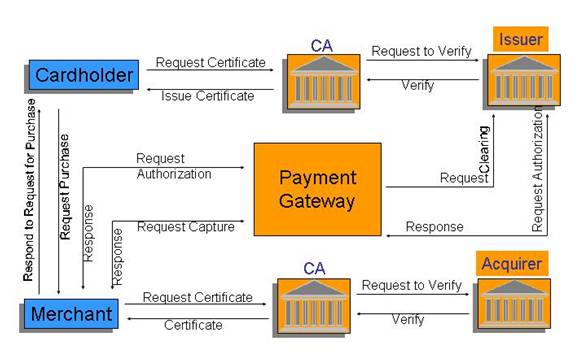
SET works
as shown in the diagram above:
- Consumer (cardholder) obtains
digital certificate from the
issuer. Note that the issuer (for
example Visa) can act as a certificate authority or an
approved certificate authority is used for the process in which case verification
of the issuer is obtained by the CA before certification of the consumer.
The consumer's digital certificate contains among other things, consumer's
public key, issuer's public key and credit details and it essentially amounts
to consumer's credit card that can be used for online payments. A software application called the digital wallet
is installed on the client. Digital
wallet stores consumer's digital certificates in encrypted form. These certificates would in turn be used
for online credit card payments. This
means that credit card information does not need to be inputted every time
consumer needs to make a purchase.
- Merchant obtains a digital
certificate from his bank (acquirer) that acts as CA or another CA that is
approved by the acquirer. There is
also another entity called the payment gateway that is set up by the
financial institutions to process online payment transactions. Payment gateways are certified by a CA
that is approved by the acquirer. Merchant's
certificate includes merchant's public key and payment gateway's public
key
- Consumer places his order to
the merchant online and consumer's browser ensures the authenticity of the
merchant through merchant's certificate that arrives at the client.
- Client's digital wallet sends
the order to the merchant. Transfer
of consumer certificate to the merchant, ensures the merchant that the
account number is valid and approved by the issuer. This so called order is in two parts:
- One part is the information
about the order (the products, services, delivery address, etc). This information is encrypted using
merchant's public key.
- The other part is the payment
information that is encrypted using payment gateway's public key.
With this strategy merchant can only access the order
information and the financial institutions can only access the payment
details. Note that SET protocol uses SSL
for the secure communication. Integrity
and non-repudiation is ensured through creation of two digital signatures, one
for the merchant (by encrypting the message digest of order information) and
the other for the issuer (by encrypting the message digest of payment
information). This concept is called the
dual
signature.
- Merchant forward the order to
the payment gateway in order to get authorisation for the payment. Authorisation is obtained from the
issuer and forwarded to the merchant.
- Merchant processes the order
and requests capture through the payment gateway
For more,
see:
http://www.tcm.hut.fi/Opinnot/Tik-110.501/1996/seminars/works/set/SET.html
http://www.setco.org/faq_usr.html
|
What's
the difference between SET and SSL? |
|
|
|
What
is SETco? |
|
|
|
What
is the improvement in protection with SET? |
|
|
|
What
are the key benefits of SET for merchants? |
|
|
|
What
is SET mark? |
|
|
|
How
can you tell if a website has SET technology? |
|
|