Perhaps you would find it surprising to know that there are a high number
of organisations (in particular the corporates) that would invest in technology
simply for the sake of investment and with no clear indication of business
goals. Why an organisation invests in deployment
of an Intranet and what the business goals are for the strategy would depend very
much on who you talk to and at what level of the organisational hierarchy they
are. For example if the question is put
to people at operational level possible answers would be
- more
efficient provision of information
- higher
quality or abundance of information
- better
connectivity among the workers through say email and collaboration forums
- Lowering
cost of transactions.
At the strategic level, executive managers may state the reasons for the
deployment of an Intranet as
- better
organisational productivity
- better
connectivity and support of sales and maintenance personnel away from the
office through provision of appropriate information
- better
personal productivity through efficient connectivity
- better
management and use of resources through centralising and sharing
- enabling
working from home
For those
goals stated at the operational level, task is predominantly of technical nature. However Intranet deployment for the type of
goals that we have stated at the strategic level requires rethinking of the
fundamental organisational structure and its building blocks. It requires an alternative working culture
where individuals are much more enabled and consequently responsible. This responsibility would be in the form of managing
their time, their resources, and their choices.
Task is no longer one of technical implementation. Implementation of Intranet without a clear
understanding of its potential benefits and much more to the point without a
clear understanding of organisational goals therefore would not result in
gaining full potentials of the investment.
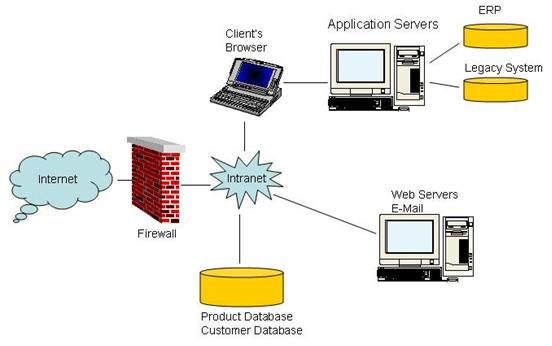
Intranet or
Internal Web (or sometimes even Internal Internet) is an internal network that
is private to the organisation and only visible to the employees. Note that Intranets do not necessarily have
to be geographically limited and that they can span the globe provided that
access is limited to the employees. Basically a Web server is employed for
internal information needs of the clients (the employees). Drivers for the Internet/Web platform are;
- It has become very common to disseminate
information using Web servers.
- Web servers are relatively easy
to set up.
- There is compatibility at the
front end when a browser is used as the client. Developer does not need to worry about
client compatibility.
- The whole idea of hypertext is
that information can be of many formats and many types, including text,
image, and multi-media.
- Adherence to Internet standards
and protocols mean ease of connectivity to the Internet and consequently;
- Remote logging in
capabilities.
- Possibility of extending to
business partners over the Internet.
- Better support of employee
away from head quarters.
- Employee empowerment.
Essentially
it is an internal network that uses Internet communication standards. TCP/IP has to come into the equation because HTTP
that Web server uses is actually a TCP/IP service. In other words HTTP uses TCP/IP for communication
on the Internet. This in essence makes
the Intranet a multi-tier client-server architecture with browser used as
the client, business logic tier is at the Web server and if applicable the
application servers, and a database or a number of database servers used for
back-end storage of data. Other elements
of the architecture that could be mentioned are the middleware components
such as the CGI, ASP, JSP scripts. Also
worth mentioning as middleware are the proprietary application programming
interfaces (APIs).
|
How
does the Intranet compare and contrast with Local Area Network? You could be
looking at a number of criteria such as security, bandwidth, geographical
scope, platform, communication protocols, connectivity, etc. |
|
|
As Intranet is likely to play a very important part as the information
infrastructure of the organisation, availability becomes an important
factor.
Intranets quite readily relate to email and they become the email
platform for the enterprise. Simple
Message transport Protocol or SMTP enables simple text messaging and it is one
of the protocols within the TCP/IP suit that Intranets inherit. In addition there is Multipurpose Internet
Mail Extensions or MIME that allows different content type including
multi-media content and streaming audio as part of the message. Intranets are internal networks that are
adhering to TCP/IP, replacing the propriety network protocols such as Novell
network. It becomes inevitable therefore
that they would also replace the proprietary mail systems such as Microsoft
MAPI in the same fashion.
Intranet technology also enables collaborative computing within the
organisation. The potential fruits of
collaboration could be;
- Sharing
of resources such as supporting knowledge material.
- Web-based
sharing of routine business documents and consequently improving work flow
efficiency.
- Online
messaging and use of email, interactive chat, video conferencing, Bulletin
boards, and screen sharing.
- Online
discussion forums.
- Integration
of data resources, databases, and legacy systems.
- Collaboration
in a secure environment.
- Search
and retrieval capabilities.
Intranets
could be designed and configured for a community of the employees. For example sales team may use an Intranet
that is private to them. The web-enabled
nature of the platform means that it can easily interface with other platforms
such as other organisational Intranets, electronic commerce platform, Internet-based
purchasing, etc.