API stands for Application Programming Interface. APIs provide the vehicle for the exchange of
data and message from one application to another or in other words they
facilitate the communication between two software programmes. One can think of APIs as tools for building
software applications or as a virtual interface between two software
applications' internetworking. Examples
of the applications could be MSExcel and MSWord. You should bear in mind that a
proposed solution or a system could comprise or at least include a number of
off-the-shelf commercial software application products. Solution could therefore be the integration
of a number of already developed and commercially based "plug-ins" and
software developed for the application at hand.
Communication between the various applications and software components
therefore become a major concern. APIs
are examples of middleware that enable these communications.
I suppose ASP and CGI scripts are also types of middleware
that could enable this type of communication and CGI have been around for quiet
sometime. Development of APIs though was
an attempt to increase the efficiency of the middleware. The fundamental difference
of API and CGI is that CGI scripts need compilation every time they are called
where as in case of API; the server invokes a single instance of the program that
is reused. Through a technique called multi-threading,
individual requests from the clients are treated as threads instead of entire
programs. The underlying idea is interoperability between the various plug-ins
and the application.
Microsoft's Internet Information Server (IIS)-s API is referred
to as ISAPI.
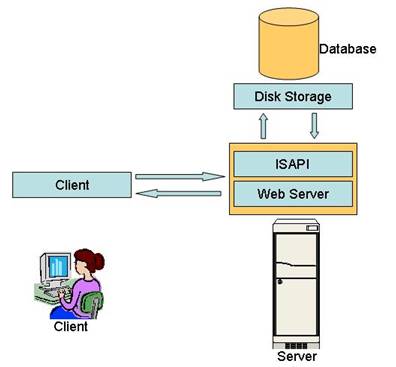
One of the examples if ISAPI is Internet Database Connector
or IDC. IDC is a component of Internet
Information Server that provides access to database capability for the
server. In this example Web browser send
s a request to the server (through HTTP).
Internet server accesses the database through a component of IDC. Respond is sent back to the client in HTML.
The Java
platform also makes extensive use of APIs.
In essence Java platform consists of the Java APIs and the Java virtual
machine (JVM). APIs are libraries of
compiled programmes that developers can use in their applications. It's all about saving time and software
reuse. These libraries let you add the
ready-made executable codes to your application programmes.