Imagine a network within
an office. There are a number of work
stations and in each we have local hard drives.
Then we have peripheral machines like printers. In a peer-to-peer (P2P) architecture each one
of the computers can be allowed access to all the other computers (other work
stations, printers, scanners, etc). All
hard disks and peripherals can be shareable between all the hosts. You have realised that I use the term 'can be'
quite often, so as to suggest that access rights have to be provided to the
hosts. For example printers could be
password protected. The way it works
is that printer is mounted on one of the machines on the network and another
machine is given access to the printer and the whole thing looks as though
printer is local to it. Good for situations
when we have a small local network and we do not want to be messing with complicated
server set-up.
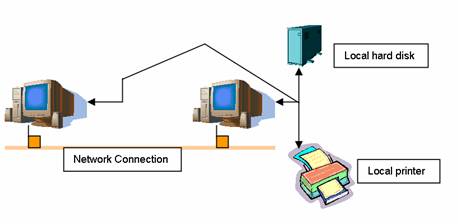
In a network like this all
machines are connected to all other machines in the network. Each machine can act as both a client and a
server. Likewise, every time a search
request is entered, it flows through all of the machines hooked into the network
— often several thousand hosts/servers with more than a million files between
them. With all those servers out there, you stand a good chance of finding
most any file you want.
|
How does client-server
differ from peer-to-peer? What are the ad/disadvantages? |
|
|
P2P is not
a new technology and it lost favour with the advent of client-server architecture.
However it is making a comeback with Internet applications and this
is predominantly thanks to ventures like Napster.
|
What is kaza famous for? In simple terms, How does
their architecture actually work? |
|
|
P2P networking
over the Internet also promises to lead the way toward new architectures for
the Internet in the form of commercial sharing of computing resources.
This type of vision is close to the original philosophy of Internet
and open source systems. Another envisaged application of P2P is in search
engines. With P2P, instead of crawling
web sites through a central database, web sites can crawl themselves and for the participants to share information
with each other and other users.
Internet
applications using P2P are not altogether free of problems. One drawback is that users must be willing to
share their bandwidth with the participants and allow access to their computers.
This has confidence and trust implications as well as security and
vulnerability to viruses and other baddies.
Integrity
of information could also be a problem. Imagine
if the track Sabbath Bloody Sabbath from Black Sabbath's Sabbath Bloody Sabbath
album in MP3 is labelled solitaire by Andy Williams.