What
is client-server architecture?
The process
of communication on the Internet and the technology and standards that Internet
rests upon are totally hidden from the user.
Interactions of users with Internet are through a number of applications
whose designs and realisations are based on client-server architecture. Client and server are two types of software
that have distinct functionalities. Internet
applications call the services of these two applications for different functionalities.
Client software usually is at the user's desktop and its job is predominantly
interaction with the user although additional functionalities are also possible
and consequently we tend to talk about thin and fat clients. Server software on the other hand resides on
a server-class machine or a workstation and its functionality could be varied
in the form of provision of a specialised service, data processing, and more than often, retrieval of data from
a database and present the findings to the client.
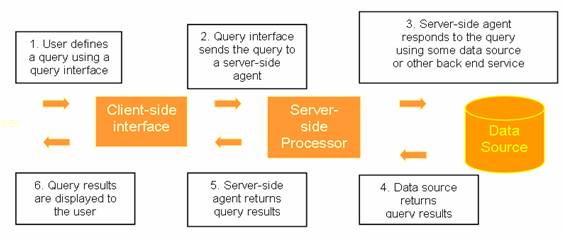
So as the
name suggests client's function is to request a service from the server and
server's job is to process the request and respond to the client. Client provides a query interface and it also
transmits the query to the server. Server
performs some server-side processing on the data that is passed on to it by
the client or data it has retrieved from a database and transmits the result
of the query back to the client. Client
may then do some client-side processing and present the results to the user.
An example
could be user authentication where client provides the vehicle for the user
to input its username and password and transmits the data to the server. Server would then query the database in order
to find a match for the combination of the data and prepare a response (yes/no)
for the client and transmit the response back to the client.
Interaction
with the user is the main function of client, however the two major clients
in the market (Internet Explorer and Netscape) can be referred to as "fat
client" as they both offer a host of features and functionalities. For example Netscape navigator is also messenger
for reading e-mail, composer for authoring
HTML pages, calendar for personal and group scheduling, etc. Likewise the explorer includes outlook express
for mail facilities, front-page express for HTML authoring, and net-meeting
for collaboration.
|
What kind of applications are suitable for client-server
architecture? |
|
|
Strictly
speaking a client-server architecture does not have to be Internet-based. LANs are also invariably
client-server or peer-to-peer.
And so there
are two issues:
- Client and server need to locate
each other
- Client and server need to communicate
with each other