By now you all know that HTML is the universal standard for presenting data on Internet. HTML is tag-based language e.g <BODY> </BODY>, you can write HTML tags and embed your data in them. Your browser interprets these HTML tags and displays the information in the browser. But with HTML you are restricted with the tags, which are already written for you.
In XML you have separate content (XML Document) & separate format (DTD)
In XML you can design your own tags, and today is your chance to do so.
For today’s exercise, you have
to write an XML file which represents the data from the Enrolment Database.
If you want to review your thoughts on HTML & XML click
here.
To download the Enrolment database click here.
Here is a snap shot of the Enrolment database
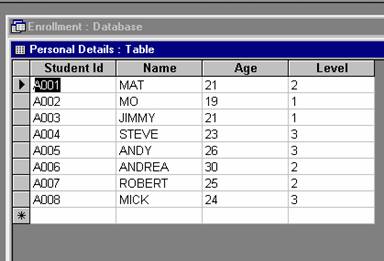
To begin your exercise you need a text editor to write your XML file.
Step one Review the Enrolment database
Step two Find the root element
Step three Determine the child elements
Step four Write the XML file, with the structure
Step five Save your XML file as student.xml extension
Step six Open your XML file in the browser to test it (if it everything is fine, and the browser doesn’t show any errors move on to step seven, otherwise check your XML file for errors)
Step
seven
Download this HTML file to the same directory where you have kept your
XML file. Open student_details.html to
see the formatted output from your XML file. (Remember XML is case-sensitive)
This is how you would describe information from a database using XML.