HTML (Hyper-Text Markup
Language) is the industry standard for presenting Web content that are designed
to be rendered by standard Web browser clients.
Very much in line with the idea of Web content and client-server
applications, WML (Wireless Markup Language) is the industry standard for
developing content that are designed to be rendered by Micro Browser clients such
as mobile phones. These clients
generally have small screens and are designed to operate over limited bandwidth
and accordingly WAP (Wireless Application Protocol) is optimised to meet this
challenge.
|
WAP is about delivering highly relevant and useful content to the
mobile users with no frills. What do we mean
by frills here? |
|
|
WAP is the standard developed
by the WAP Forum for wireless and
telephony information services. These
Internet standards are designed to run on top of IP protocols. WML (wireless markup language) is XML-compliant
which means that it is interoperable.
This is important due to the numerous types and manufacturers of
handheld devices and wireless technologies.
|
WML
is XML. HTML is XML. What do we mean by these two statements? |
|
|
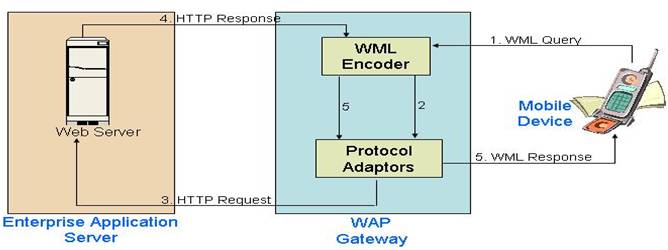
The diagram above depicts
the architecture that enables provision of WAP content. In this case user is submitting a request for
information by filling in a WML form.
Request is forwarded to the WAP gateway where it is recieved, validated,
converted into a standard HTTP request, and forwarded to the Web server that
holds the required resources. Having
recieved the HTTP request, Web server through the execution of some middleware
script (Examples: ASP script, JSP script, etc) retrives the required
information and forwards its HTTP response to the gateway. This HTTP response which in essence is a WML
page is recieved, validated, and forwarded by the gateway to the hand-held
device. Device's browser renders the WML
and displays the content.
Enabling the enterprise
infrastructure with wireless technology therefore is straight forward. This process is simplified if the
infrastructure is XML-based. The
requirement under these circumstances would be the introduction of a server
layer called the WAP gateway whose functionality would be to encode and decode
data from/to the handheld device.
Introduction and maintanence of this server layer could be expensive which
prompts many of the enterprises to opt for hosting their wireless applications
with Application Service Providers that offer WAP gateway services. Worth mentioning that introduction of the
layer does not effect the back end since Web server acts as the contact point.
Also note that organisation
would only opt for this technology if they have imminent use for it. The greatest risk is the development of new
technology which usually results in current wireless soloution to become obsolete. This means that the design of infrastructures
for long-term strategies should be flexible enough to accomodate the emerging
technologies.
WAP/WML is the established
patform in
|
General
opinion is that WAP never made the critical mass and as such was not an
economically successful technology.
What do we mean by "making the critical mass"? Why was WAP not economically successful? |
|
|
To explore more look up:
Ο WMLScript- Similar to JavaScript that is used to
extend HTML Web pages, WMLScript provides basic programming functionality that
are used to optimise the minimal usage of memory.
Ο WAE (Wireless Access Environment)- This is equivalent to DNA in Microsoft n-tier
architecture.