What is online payment processing?
This document discusses the following topics
l
Online Payment Processing Basics
–
The Payment Processing Network
–
How Payment Processing Works
l
What You Should Know About Fraud
l
What to Look for in a Payment Processing Solution
Basics – Payment Processing
l
For payment processing to work correctly
–
merchants must connect to
a network of banks (both acquiring and issuing banks), processors, and other
financial institutions so that payment information provided by the customer
can be routed securely and reliably.
–
The solution is a payment gateway that connects your
online store to these institutions and processors. Because payment information
is highly sensitive, trust and confidence are essential elements of any payment
transaction.
–
This means the gateway should be provided by a company
with in depth experience in payment processing and security.
Payment Processing Network
l
Acquiring Bank
–
In the online payment processing
world, an Acquiring Bank provides Internet Merchant Accounts.
–
A merchant must open an Internet
Merchant Account with an Acquiring Bank to enable online credit card authorization
and payment processing. Examples of Acquiring Banks include
–
Merchant eSolutions and most
major banks.
l
Internet Merchant Account
–
A special account with an
Acquiring Bank that allows the merchant to accept credit cards over the Internet.
–
The merchant typically pays
a processing fee for each transaction processed, also known as the discount
rate.
–
A merchant applies for an
Internet Merchant Account in a process similar to applying for a commercial
loan.
l
Authorization
–
The process by which a customer's
credit card is verified as active and that they have the credit available
to make a transaction.
–
In the online payment processing
world, an authorization also verifies that the billing information the customer
has provided matches up with the information on record with their credit card
company.
l
Merchant
–
Someone who owns a company
that sells products or services.
l
Payment Gateway
–
A service that provides connectivity
among merchants, customers, and financial networks to process authorizations
and payments
–
The service is usually operated
by a third-party provider
l
Credit Card Association
–
A financial institution that
provides credit card services that are branded and distributed by Customer
Issuing Banks. Examples include Visa® and MasterCard ®
l
Customer
–
The holder of the payment
instrument such as credit card, debit card, or electronic check.
l
Processor
–
A large data center that processes
credit card transactions and settles funds to merchants.
–
The processor is connected
to a merchant's site on behalf of an Acquiring Bank via a Payment Gateway.
l
Settlement
–
The process by which transactions
with authorization codes are sent to the processor for payment to the merchant.
Settlement is a sort of electronic bookkeeping procedure that causes all funds
from captured transactions to be routed to the merchant's acquiring bank for
deposit.
l
Customer Issuing Bank
–
A financial institution that
provides a customer with a credit card or other payment instrument.
–
Examples include Citibank,
Suntrust, etc.
–
During a purchase, the Customer
Issuing Bank verifies that the payment information submitted to the merchant
is valid and that the customer has the funds or credit limit to make the proposed
purchase.
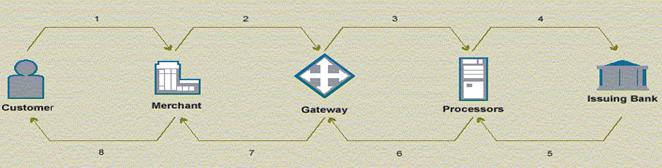
How Payment Processing Work?
Payment processing in the online world is similar to payment processing
in the offline or “Brick and Mortar” world, with one significant exception.
In the online world, the card is “not present” at the transaction. This means
that the merchant must take additional steps to verify that the card information
is being submitted by the actual owner of the card. Payment processing can
be divided into two major phases or steps: authorization and settlement.
Authorization verifies that the card is active and that the customer has
sufficient credit available to make the transaction.
Settlement involves transferring money from the customer’s account to the
merchant’s account.
Payment Processing – Authorization (Online)
l
Customer decides to make a purchase on Merchant’s Web
site, proceeds to check-out and inputs credit card information.
l
The Merchant’s Web site receives customer information
and sends transaction information to Payment Gateway.
l
Payment Gateway routes information to the Processor.
l
Processor sends information to the Issuing Bank of the
Customer’s credit card.
l
Issuing Bank sends transaction result (authorization
or decline) to the Processor.
l
Processor routes transaction result to the Payment Gateway.
l
Payment Gateway passes result information to Merchant.
l
Merchant accepts or rejects transaction and ships goods
if necessary. Because this is a “Card Not Present” transaction, the Merchant
should take additional precautions to ensure that the card has not been stolen
and that the customer is the actual owner of the card. See the “What You Should
Know About Fraud” section for more information on
preventing fraudulent transactions.
Payment Processing – Authorization (Brick and Mortar)
l
Customer selects item(s) to purchase, brings them to
cashier, and hands credit card to Merchant.
l
Merchant swipes card and transfers transaction information
to a point of sale terminal.
l
Point of sale terminal routes information to the Processor
via dial-up connection (for the purposes of the graphic above, the point of
sale terminal takes the place of the Payment Gateway in the offline world).
l
Processor sends information to the Issuing Bank of the
Customer's credit card.
l
Issuing Bank sends transaction result (authorization
or decline) to the Processor.
l
Processor routes transaction result to the point of sale
terminal.
l
Point of sale terminal shows Merchant whether the transaction
was approved or declined.
l
Merchant tells the Customer the outcome of the transaction.
If approved, Merchant has the Customer sign the credit card receipt and gives
the item(s) to the Customer.
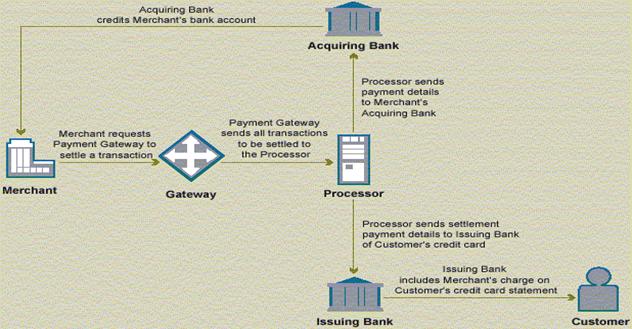
Payment Processing —Settlement
The settlement process transfers authorized funds for a transaction from
the customer’s bank account to the merchant’s bank account. The process is
basically the same whether the transaction is conducted online or offline.
What You Should Know About Fraud
l
Credit card fraud can be a significant problem for
–
customers,
–
merchants, and
–
credit card issuers.
l
Liability for fraudulent transactions belongs to the
credit card issuer for a card-present, in-store transaction, but shifts to
the merchant for “card not present” transactions, including transactions conducted
online. This means that the merchant does not receive payment for a fraudulent
online transaction.
l
Fortunately, there are steps you can take to significantly
limit your risk as an online merchant.
l
Choose a payment services provider that is well established
and credible. Your provider should also have in-depth experience in and a
strong track record for transaction security.
l
Make sure your payment gateway provider offers real-time
credit card authorization results. This will ensure that the credit card has
not been reported as lost or stolen and that it is a valid card number.
l
One of the simplest ways to reduce the risk of a fraudulent
transaction is to use Address Verification Service (
l
Use Card Security Codes (Cardholder Identification), known as CVV2 (Card verification Value) for Visa,
CVVC for MasterCard, and
–
For American Express, the code is a four digit number
that appears on the front of the card above the account number.
–
For Visa and MasterCard, the code is a three-digit number
that appears at the end of the account number on the back of the card.
–
The code is not printed on any receipts and provides
additional assurance that the actual card is in possession of the person submitting
the transaction.
–
As a merchant, you can ask for this code on your online
order form.
–
Even if you do not use this for processing, simply asking
for it acts as a strong deterrent against fraud.
l
Watch for multiple orders for easily resold items such
as electronic goods purchased on the same credit card.
l
Develop a negative card and shipping address list and
crosscheck transactions against it. Many perpetrators will go back to the
same merchant again and again to make fraudulent transactions.
What to Look for in a Payment Processing Solution
l
Finding a reliable, secure, and flexible payment processing
solution for your business is critical, so it’s important to take the time
to investigate and assess the options available to you. A payment processing
solution should:
–
Reliably and cost-effectively accept and process a variety
of payment types, including credit cards and electronic checks. Not only does
this reduce lost sales, but it also enhances the quality of your site by allowing
your customers the freedom and flexibility to pay you quickly and conveniently.
–
Provide real-time credit card authorization results allowing
you to accept or reject orders immediately and reduce the risk of fraudulent
transactions.
–
Easily track and manage payments from multiple payment
types or processors so you can spend more time on your business, not on managing
transactions.
–
Be able to act as a virtual terminal to allow for processing
offline transactions.This gives you the flexibility to process orders received
via telephone, fax, e-mail, or in person.
–
Provide and store transaction records letting you to
easily search for transactions and create transaction reports.
–
Scale rapidly and seamlessly to accommodate increased
transaction volumes so your systems grow as your business grows.
–
Provide flexible, easy integration with the Merchant's
Web site. The sooner you can start accepting payments, the sooner you start
generating revenue from your site.
–
Be able to work with all the leading Internet Merchant
Accounts, which allows you to switch your banking relationship and not have
to worry about installing new software or performing new integrations.
–
Be provided by a well-established and trustworthy company.
This ensures that your payment service provider will continue to provide reliable
payment services as well as new features.
|
Trust
Commerce, Merchant commerce,
and Authorize.net are three
comapnies that provide online payment soloutions. Look them up and make
notes about their services. |
|
|